 |
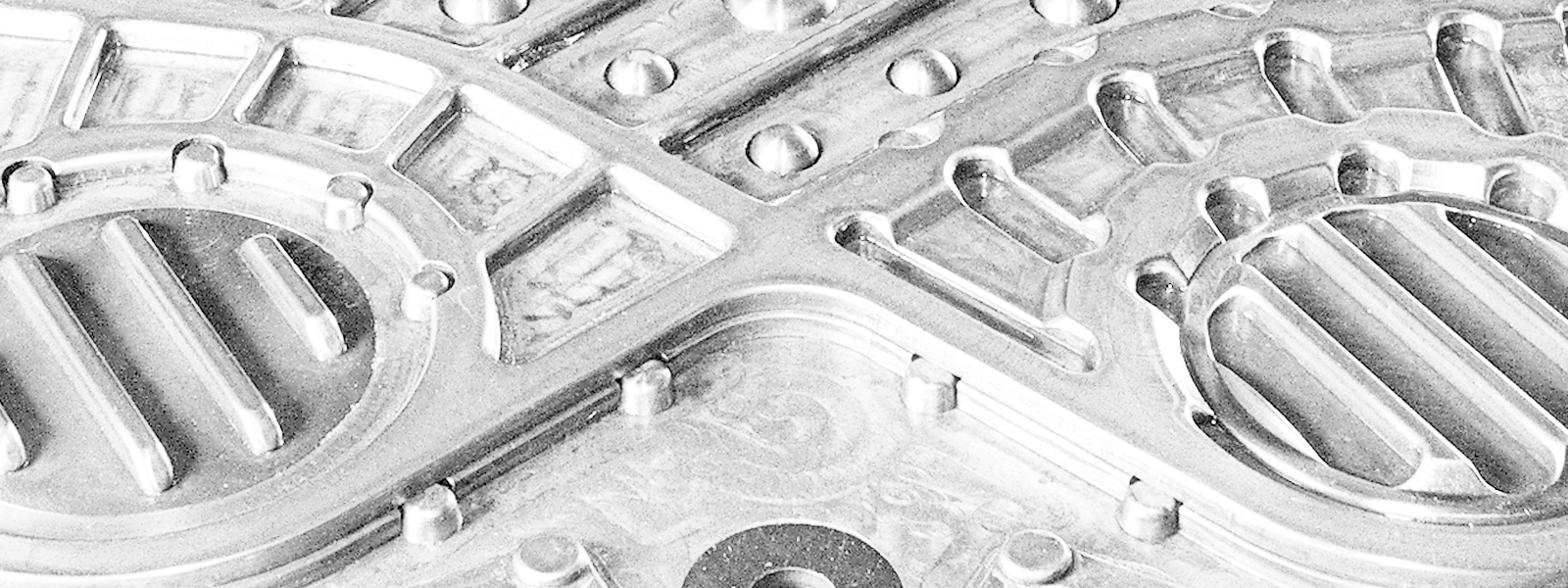
Free Flow (FF)
Free Flow (FF)
The EUROCAL 32 FF und EUROCAL 61 FF Free Flow Plate Heat Exchangers make it possible to thermally treat materials with proportions of solids in them such as, for example, juices with small particles of fruit, sauces, and fruit yoghurt.
The flow of liquids that contain fibrous material can lead to the solid particles sticking which interferes with the free flow of the product. The plates of conventional heat exchangers are usually built in such a way that they touch and support each other at numerous points. When this happens, the function of a conventional heat exchanger is affected or even becomes impossible.
The free flow plates have a wave profile running perpendicular to the direction of flow under which the waves of adjacent plates do not touch each other but stand parallel to one another. In this way, free passage for both media engaged in the exchange of heat is set up.
Since the free flow plate heat exchanger is not susceptible to contamination, this device is well suited for all industries that operate with highly contaminated liquids or liquids with high fiber content.
In order to give the plate channels the necessary pressure resistance, the middle part of the plate exhibits 3 to 5 flow fields that are separated by supporting ribs running in the longitudinal direction of the plates.
Evaporation plate (SP)

Evaporation plate (SP)
The narrower flow channels in the lower part of the plate assure turbulent flow and thus, an efficient heating. Toward the top, the flow channels widen as a result of which light and quick vaporisation is achieved. The size and position of the entry and exit holes are also configured in such a way that the medium is distributed optimally.
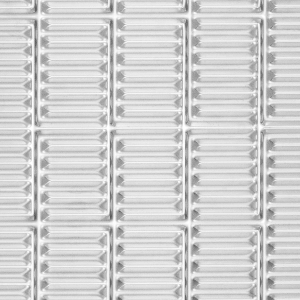
Combi Flow (CF)
Combi Flow (CF)
Thirty years ago, Fischer developed the revolutionary COMBI FLOW® System. It is the first system with two different flow characteristics in one unit. The COMBI FLOW System consists of two types of plates: the X plate and the Z plate. When two X or two Z plates are lined up against each other, a “soft channel” results which means less pressure loss. The combination of an X and a Z plate forms a “hard channel” which means greater heat transfer.
This novel system makes it possible, for the first time, to achieve optimal heat transfer on two heat transfer sides, even under the most different flow rates. Because of the worldwide success of the "COMBI FLOW System”, Fischer developed additional highly specialised profile types: OMNI FLOW | VARIOS FLOW | DOUBLE (DUAL) FLOW | MULTI FLUX (MF). Like the COMBI FLOW System, the MULTI FLUX System can achieve different flow conditions for the two media, as a result of which better adaptation to their respective operational demands can be achieved. The result is a superior thermal effect compared to conventional heat exchangers with identical heat exchange surfaces.
The difference between the COMBI FLOW and MULTI FLUX systems lies in the industry in which each applied. Depending on the desired operational demands and the consistency of the media flowing through the heat exchanger, either the one or the other system is installed in order to achieve optimal performance in each case. For the MULTI FLUX System, two types of heat exchanger plates are used. They differ in the angle at which the profiles are set opposite to one another. If one aligns two identical plates together at 180°, a parallel running flow channel (soft circuit) with low turbulence results.
This configuration enables the flow of large amounts of liquid under low flow resistance and higher heat transfer coefficient. By combining two dissimilar plate types (hard circuit), turbulence results because of the crossing of the waves. That is how one can achieve a high heat transfer coefficient at low flow rates. When does the MULTI FLUX System bring special advantages? (see advantages of the COMBI FLOW System)
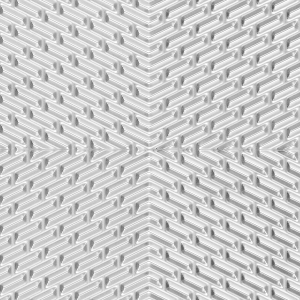
Varios Flow (VF)
Varios Flow (VF)
The VARIOS FLOW System offers the enhanced possibility of “hard” and “soft” circuits. This system is assembled from a combination of two types of profiles, the FISCHBONE HARD (FH) and the UNIWAVE HARD (UH) profiles. Because of the unique profile configuration, two new plate channels result.
The VARIOS FLOW Profile is best suited for plants which operate with media of highly variable viscosity and flow quantities.
Fishbone soft (FW)
Fishbone soft (FW)
The FISCHBONE profile is distinguished by a high thermal efficiency. The FISCHBONE SOFT is distinguished from the FISCHBONE HARD’s profile through its different angles within the profile. As with the COMBI FLOW system, either a “soft” or a “hard” channel emerges. The former means less pressure drop while the latter affords greater heat transfer. A combination of both plates in one system, as with the COMBI FLOW, VARIOS FLOW and MULTI FLUX systems is, however, not possible.
Fishbone hard (FH)
Fishbone hard (FH)
The FISCHBONE HARD profile is distinguished by high thermal efficiency. The FISCHBONE HARD differs from the FISCHBONE SOFT through the variable angle within the profile. As with the COMBI FLOW system, either a “soft” or a “hard” channel results. The former means less pressure drop while the latter affords a higher heat transfer. A combination of both plates in one system, as with the COMBI FLOW, VARIOS FLOW and MULTI FLUX systems is, however, not possible.
Double (Dual) Flow (DF)
Double (Dual) Flow (DF)
The DOUBLE (DUAL) FLOW profile represents a further development of the COMBI FLOW profile that has been proven over many years. The profiles are distinguished by defining “A” and “V” profiles. The varying combination of the two profiles can be used as in the COMBI FLOW System in order to produce a hard or a soft channel. Accordingly, the pressure drop can be reduced or the heat transfer increased.
Heat retention plate (HH)
Heat retention plate (HH)
The heat retention plate is not a heat exchanger plate in the usual sense. Its purpose lies in holding a specific temperature. The heat retention plates are integrated, if necessary, into our heat exchangers as a plate pack of its own. The advantage in comparison to conventional heat retention tubes lies in the fact that the plate pack is much more compact so that it can be integrated better and additional insulation is no longer necessary.
Uniwave hard (UH)
Uniwave hard (UH)
The UNIWAVE HARD profile consists of an additional interruption of the waves, as a result of which the flow cross-section changes. The flow cross-section thereby becomes broader while the plate remains the same size.
Wave profile (W)
Wave profile (W)
The WAVE PROFILE provides an especially soft profile with low pressure drop.




